Clusters de necessidades psicológicas e perfis motivacionais na educação física escolar e seus impactos na saúde mental de adolescentes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12820/rbafs.30e0389Palabras clave:
Atividade motora, Transtorno de humor, Sintomas afetivoResumen
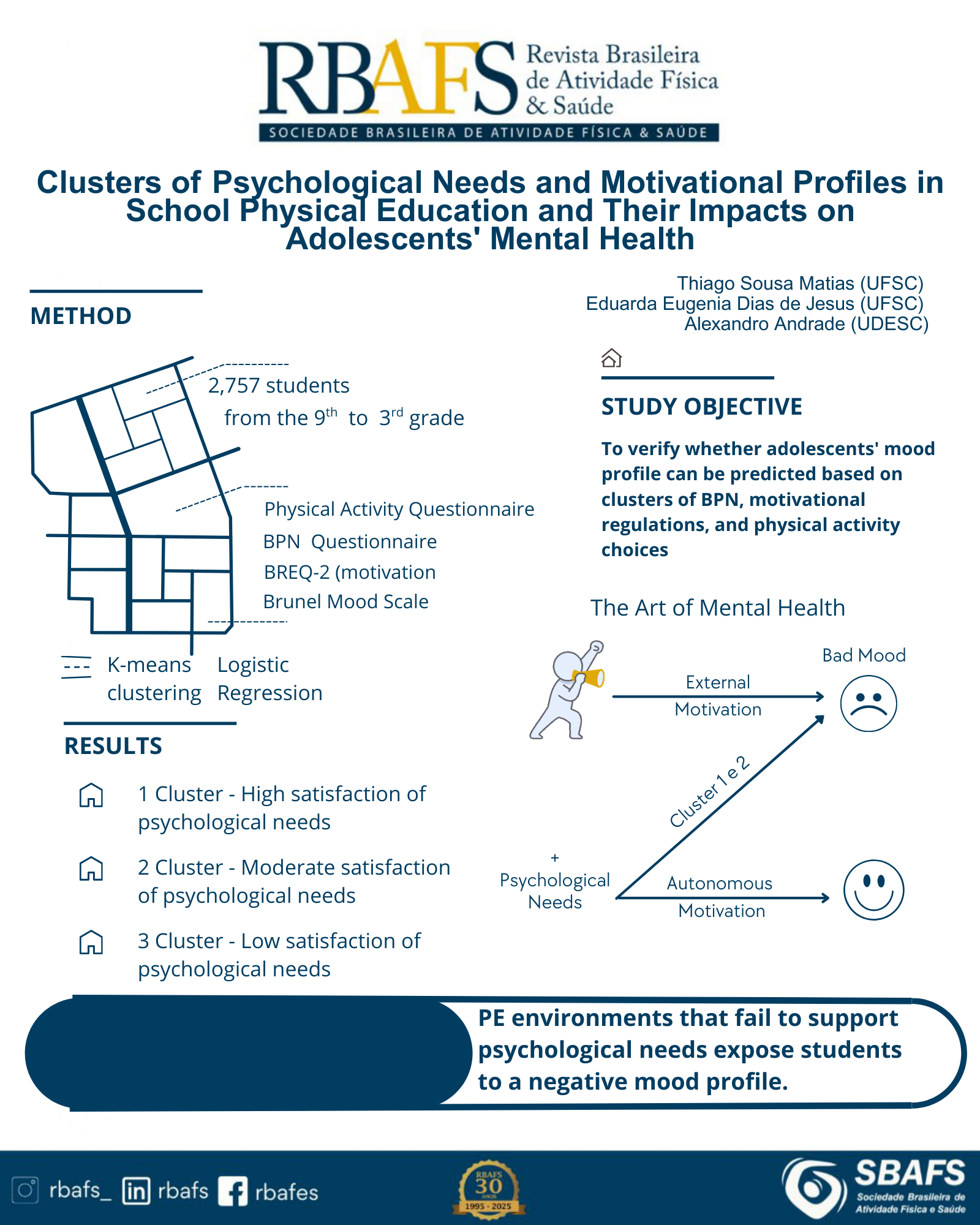
Introdução: A teoria da autodeterminação destaca a importância da satisfação para as necessidades psicológicas básicas (NPB (autonomia, competência e vínculo) para a motivação e o bem-estar psicológico. Na Educação Física (EF), ambientes que apoiam essas necessidades estão associados a resultados positivos, enquanto ambientes que as frustrações podem levar a resultados desadaptativos. Objetivo: Verificar se o perfil de humor pode ser predito com base em Cluster de NPB em EF, regulações motivacionais e escolhas de atividade física (AF). Método: Estudo transversal de base populacional com 2.757 adolescentes estudantes (15 ± 4 anos) selecionados proporcionalmente ao tamanho populacional da Grande Florianópolis/Santa Catarina. Questionários avaliaram as NPB, as regulações motivacionais, as escolhas de AF e o perfil de humor. Os estudantes foram divididos em três Clusters com base em seus perfis de NPB na EF: Cluster 1 (positivo) relatou alta satisfação das NPB; Cluster 2 (intermediário) apresentou satisfação moderada; Cluster 3 (negativo) experimentou baixa satisfação e frustração das NPB. Os dados foram analisados por estatísticas descritivas e inferenciais. Resultados: Os Clusters 3 (negativo) e 2 (intermediário), em comparação com os Cluster 1 (positivo), tiveram três e duas vezes mais chances de ter um perfil de humor negativo, respectivamente. A escolha de AF aumentou as razões de prevalência de risco para o Cluster 3 (OR = 3,81; 95% CI = 2,52 – 5,75). A regulação identificada (OR = 0,80; 95% CI = 0,67 – 0,95) e a regulação intrínseca (OR = 0,83; 95% CI = 0,72 – 0,96) reduziram ligeiramente a associação negativa entre Cluster 2 e 3 e foram associadas a um perfil de humor positivo. Conclusão: Ambientes de EF que não satisfazem as NPB expõem os estudantes a um perfil de humor negativo. Escolhas de AF relacionadas a um locus de controle externo podem agravar essa condição. No entanto, a regulação motivacional interna, especialmente as regulações intrínseca e identificada, parece promover um humor positivo.
Descargas
Citas
Tendinha R, Alves MD, Freitas T, Appleton G, Gonçalves L, Ihle A, et al. Impact of Sports Education Model in Physical Education on Students' Motivation: A Systematic Review. Children (Basel). 2021;8(7):588. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/children8070588
Palmer K, Robbins LB, Ling J, Kao TA, Voskuil VR, Smith AL. Adolescent Autonomous Motivation for Physical Activity: A Concept Analysis. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020;54:e36-e46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2020.04.020
Burgueño R, García-González L, Abós Á, Sevil-Serrano J. Students’ motivational experiences across profiles of perceived need-supportive and need-thwarting teaching behaviors in physical education. Phys Educ Sport Pedagogy. 2024;29:82–96. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17408989.2022.2028757
Erdvik IB, Haugen T, Ivarsson A, Säfvenbom R. Global Self-Worth among Adolescents: The Role of Basic Psychological Need Satisfaction in Physical Education. Scand. J Educ Res. 2020;64:768–81. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00313831.2019.1600578
Hall J, Jones L, Robertson G, Hiley R, Nathwani D, Perry MR. 'The Mould that Changed the World': Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of children's knowledge and motivation for behavioural change following participation in an antimicrobial resistance musical. PLoS One. 2020;15(10):e0240471. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240471
Baena-Extremera A, Ruiz-Montero PJ, Hortigüela-Alcalá D. Neuroeducation, Motivation, and Physical Activity in Students of Physical Education. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(5):2622. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052622
Wu X, Gai X, Yu T, Yu H, Zhang Y. Perceived Motivational Climate and Stages of Exercise Behavior Change: Mediating Roles of Motivation Within and Beyond Physical Education Class. Front Psychol. 2021;12:737461. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.737461
Cuevas-Campos R, Fernández-Bustos JG, González-Cutre D, Hernández-Martínez A. Need Satisfaction and Need Thwarting in Physical Education and Intention to be Physically Active. Sustainability. 2020;12(18):7312. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187312
Gómez-López M, Chicau Borrego C, Marques da Silva C, Granero-Gallegos A, González-Hernández J. Effects of Motivational Climate on Fear of Failure and Anxiety in Teen Handball Players. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(2):592. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020592
Duffey K, Barbosa A, Whiting S, Mendes R, Yordi Aguirre I, Tcymbal A, et al. Barriers and Facilitators of Physical Activity Participation in Adolescent Girls: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. Front Public Health. 2021;9:743935. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.743935
Rodrigues F, Teixeira DS, Neiva HP, Cid L, Monteiro D. The bright and dark sides of motivation as predictors of enjoyment, intention, and exercise persistence. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30:787–00. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13617
Bae MH. Happiness Levels and Leisure Life Satisfaction for Sports Leisure Activities Participation: Implication for Physical Education in Korea. Iran J Public Health. 2022;51(9):2007-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18502/ijph.v51i9.10555
Jetzke M, Mutz M. Sport for Pleasure, Fitness, Medals or Slenderness? Differential Effects of Sports Activities on Well-Being. Appl Res Qual Life. 2020;15:1519–34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-019-09753-w
Kralova K, Fialova L. Analysis of adolescent satisfaction with the quality of their physical education classes. Hung Educ Res J. 2021;11:31–42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1556/063.2021.00020
Rojo-Ramos J, Franco-García JM, Mayordomo-Pinilla N, Pazzi F, Galán-Arroyo C. Physical Activity and Emotional Regulation in Physical Education in Children Aged 12–14 Years and Its Relation with Practice Motives. Healthcare. 2023;11:1826. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11131826
Navarro J, Escobar P, Miragall M, Cebolla A, Baños RM. Adolescent Motivation Toward Physical Exercise: The Role of Sex, Age, Enjoyment, and Anxiety. Psychol Rep. 2021;124:1049–69. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0033294120922490
Martinez A G, Gietzen L, McDaniel VF. Exploring the Role of Physical Activity Influencing Emotional Regulation and Mental Health in Adolescents. Pac J Health. 2024;7(1):1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.56031/2576-215X.1046
Luiz RR, Magnanini MMF. A lógica da determinação do tamanho da amostra em investigações epidemiológicas. Cad. Saude Colet.2000;8(2):9–28.
Florindo AA, Romero A, Peres SV, Silva MV, Slater B. Desenvolvimento e validação de um questionário de avaliação da atividade física para adolescentes. Rev Saude Publica. 2006;40:802–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89102006000600009
Pires A, Cid L, Borrego C, Alves J, Silva C. Validação preliminar de um questionário para avaliar as necessidades psicológicas básicas em Educação Física. Motricidade. 2010:6:33–51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.6063/motricidade.6(1).157
Markland D, Tobin V. A Modification to the Behavioural Regulation in Exercise Questionnaire to Include an Assessment of Amotivation. J Sport Exerc Psychol.2004;26:191–6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.26.2.191
Rohlfs ICP de M, Rotta TM, Luft CDB, Andrade A, Krebs RJ, Carvalho T. A Escala de Humor de Brunel (Brums): instrumento para detecção precoce da síndrome do excesso de treinamento. Rev Bras Med Esporte. 2008;14(3):176–81. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-86922008000300003
Romero-Parra N, Solera-Alfonso A, Bores-García D, Delfa-de-la-Morena JM. Sex and educational level differences in physical activity and motivations to exercise among Spanish children and adolescents. Eur J Pediatr. 2022;182:533–42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-022-04742-y
Deci EL, Ryan RM. The ‘What’ and ‘Why’ of Goal Pursuits: Human Needs and the Self-Determination of Behavior. Psychol Inq. 2000;11:227–68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01
Vasconcellos D, Parker PD, Hilland T, Cinelli R, Owen KB, Kapsal N, et al. Self-determination theory applied to physical education: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Educ Psychol. 2020;112:1444–69. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000420
Valero-Valenzuela A, Huescar E, Núñez JL, Conte L, Léon J, Moreno-Murcia JA. Prediction of Adolescent Physical Self-Concept through Autonomous Motivation and Basic Psychological Needs in Spanish Physical Education Students. Sustainability. 2021;13:11759. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111759
Hutmacher D, Eckelt M, Bund A, Steffgen G. Does Motivation in Physical Education Have an Impact on Out-of-School Physical Activity over Time? A Longitudinal Approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:7258. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197258
Kleitsch B, Hodges Kulinna P. Tracking Student Outcomes Through Instructional Choices in Physical Education. The Physical Educator. 2022;79:491–513. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18666/TPE-2022-V79-I5-11294
Cachón-Zagalaz J, Carrasco-Venturell H, Sánchez-Zafra M, Zagalaz-Sánchez ML. Motivation toward Physical Activity and Healthy Habits of Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Children. 2023;10:659. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040659
De Meyer J, Soenens B, Aelterman N, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Haerens L. The different faces of controlling teaching: implications of a distinction between externally and internally controlling teaching for students’ motivation in physical education. Phys Educ Sport Pedagogy. 2016;21:632–52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17408989.2015.1112777
Zeleke, E. A., Fikadu, T., Bekele, M., Sidamo, N. B. & Temesgen Worsa, K. Physical activity status among adolescents in Southern Ethiopia: A mixed methods study. PLoS One. 2023;18:e0293757. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0293757
Nogg KA, Vaughn AA, Levy SS, Blashill AJ. Motivation for Physical Activity among U.S. Adolescents: A Self-Determination Theory Perspective. Ann Behav Med. 2021; 55:133143. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/abm/kaaa037
Koka A, Tilga H, Kalajas-Tilga H, Hein V, Raudsepp L. Perceived Controlling Behaviors of Physical Education Teachers and Objectively Measured Leisure-Time Physical Activity in Adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16:2709. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152709
Matias TS, Andrade A, Manfrin JM. Regulações motivacionais das diferentes escolhas de atividade física no lazer de adolescentes. Rev Bras Ativ Fís Saúde. 2019;24:1–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12820/rbafs.24e0088
Öktem T, Çingöz YE. The Effect of Motivation to Participate in Sports on Happiness Level in University Students. Educ Q Rev.2023;6:1-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31014/aior.1993.06.01.715
Matias TS, Costa BR, Nienov GTA, Alves JF, Andrade A. A exposição e a manutenção para a prática de atividade física estão associadas à saúde mental de adolescentes. Coleç Pesqui Educ Fís. 2020;19:7–15.
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 Thiago Sousa Matias, Eduarda Eugenia Dias de Jesus, Alexandro Andrade

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Al enviar un manuscrito a la Revista Brasileira de Atividade Física & Saúde, los autores mantienen la titularidad de los derechos de autor sobre el artículo y autorizan a la Revista Brasileira de Atividade Física & Saúde a publicar este manuscrito bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución 4.0 e identificarla como el vehículo de su publicación original.


