Effects of a recreational sport intervention associated with nutritional counseling on cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents: a study protocol of a randomized clinical trial
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12820/rbafs.30e0403Keywords:
Adolescent, Cardiovascular health, Food guide, Exercise, SportsAbstract
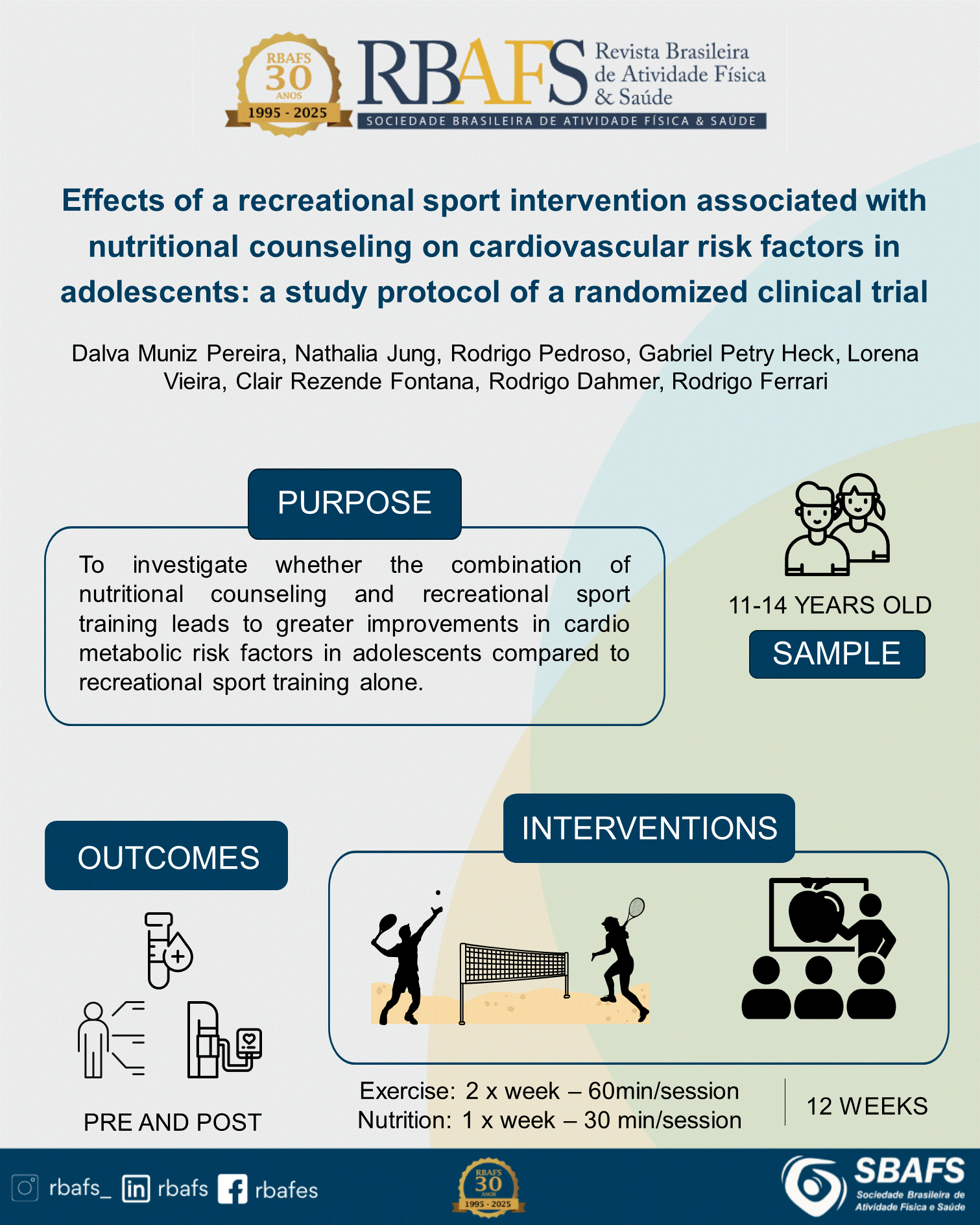
Introduction: Physical activity can provide cardiovascular and metabolic benefits in youth, and adequate nutrition provides the necessary nutrients to meet the demands of growth and development in childhood and adolescence, impacting health-related outcomes. Objective: To investigate whether the combination of nutritional counseling and recreational sport leads to greater improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors in adolescents compared to recreational sport alone. Methods: This study will be a randomized, parallel group, two-arm, superiority trial. Forty teenagers aged between 11 and 14 years old will be divided into two groups: sports training + nutritional counseling group and active control group, which will only perform sports training. Sessions will be held two days a week and will last 12 weeks. The following parameters will be evaluated pre- and post-intervention: High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL-C) (Primary outcome), total cholesterol and fractions, triglycerides, glucose, insulin, 25-hydroxyvitamin-D, C-reactive protein, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, body mass index, body fat percentage, lean mass percentage, food intake, muscle strength, and cardiorespiratory demand. Primary and secondary outcomes will be analyzed using a generalized estimating equation model for correlated measures, and adjustment for multiple comparisons will be accomplished using the sequential Bonferroni test. Final considerations: It is expected that the multidisciplinary strategy, with the association of nutrition and physical activity, will be more effective than the isolated intervention in physical activity in the primary stages of the study, evidencing the positive effect of the combined approach on the cardiovascular health of adolescents.Trial registration: Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials (ReBEC): RBR-10bfs3gm.
Downloads
References
Sultana S, Rahman MM, Sigel B, Hashizume M. Associations of lifestyle risk factors with overweight or obesity among adolescents: a multicountry analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;113(3):742–50.
2. Nunes MILB, Matos AGM, Lima LEM, Brito-Neto JGD. Atividade física como prevenção da obesidade e síndrome metabólica na infância e adolescência: uma revisão integrativa. Multidiscip Rev. 2021;4:e2021009.
3. Fanelli E, Abate Daga F, Pappaccogli M, Eula E, Astarita A, Mingrone G, et al. A structured physical activity program in an adolescent population with overweight or obesity: a prospective interventional study. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2022;47(3):253–60.
4. Mendonça FR, Faria WF, Silva JM, Massuto RB, Santos GC, Corrêa RC, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise combined with resistance training on health-related physical fitness in adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2022 Apr;20(2):182–9.
5. Song Y, Shi C. Association between sports participation and overall health in children and adolescents. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2023;51:101718.
6. Torres W, Cayres-Santos SU, Urban JB, Moraes-Chagas LG, Christofaro DGD, Turi-Lynch BC, et al. Participation in non-professional sports and cardiovascular outcomes among adolescents: ABCD Growth Study. Matern Child Health J. 2020;24(6):787–95.
7. Wilson OWA, Whatman C, Walters S, Keung S, Enari D, Rogers A, et al. The value of sport: wellbeing benefits of sport participation during adolescence. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8579.
8. Kupka R, Siekmans K, Beal T. The diets of children: overview of available data for children and adolescents. Glob Food Sec. 2020;27:100442.
9. Rocha NP, Milagres LC, Longo GZ, Ribeiro AQ, Novaes JF. Association between dietary pattern and cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents: a systematic review. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2017;93:214–22.
10. Cadenas-Sanchez C, Medrano M, Arenaza L, Amasene M, Osés M, Labayen I. Association between Mediterranean dietary pattern and breakfast quality with physical fitness in school children: the HIIT Project. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1353.
11. Grace J, Biggs C, Naicker A, Moss S. Effect of physical activity and nutrition education on body mass index, blood pressure and biochemical variables in overweight and obese adolescents. Ann Glob Health. 2021;87(1):9.
12. Morgado MC, Sousa M, Coelho AB, Vale S, Costa JA, Seabra A. Effects of “Football and Nutrition for Health” program on body composition, physical fitness, eating behaviours, nutritional knowledge, and psychological status among 7 to 10 years school children. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1251053.
13. Zhao L, Dong X, Gao Y, Jia Z, Han S, Zhang J, Gao Y. Effects of exercise combined with diet intervention on body composition and serum biochemical markers in adolescents with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2022;35(11):1319–36.
14. Hassan MA, Cao Y, Li X, Ji M, Zhao M. The effectiveness of physical activity interventions on blood pressure in children and adolescents: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2024;13(5):699–708.
15. Torres W, Maillane-Vanegas S, Urban JB, Fernandes RA. Impact of sports participation on cardiovascular health markers of children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Clin Pediatr. 2022;11(4):375–84.
16. Capra ME, Monopoli D, Decarolis NM, Giudice A, Stanyevic B, Esposito S, et al. Dietary models and cardiovascular risk prevention in pediatric patients. Nutrients. 2023;15(16):3664.
17. Chan AW, Tetzlaff JM, Gøtzsche PC, Altman DG, Mann H, Berlin JA, et al. SPIRIT 2013 explanation and elaboration: guidance for protocols of clinical trials. BMJ. 2013;346:e7586.
18. Cuschieri S. The CONSORT statement. Saudi J Anaesth. 2019 Apr;13(Suppl 1):S27–30.
19. Marques DCS, Moraes LRS, Marques MGS, Ryal JJ, Santos IC, Lalucci MPPS, et al. Effects of 12 weeks of family and individual multidisciplinary intervention in overweight and obese adolescents under cardiometabolic risk parameters: a clinical trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(20):6954.
20. Borges RB, Mancuso ACB, Camey SA, Leotti VB, Hirakata VN, Azambuja GS, et al. Power and Sample Size for Health Researchers: uma ferramenta para cálculo de tamanho amostral e poder do teste voltado a pesquisadores da área da saúde. Clin Biomed Res. 2021;41(2):247-53.
21. Davidson MC, Amso D, Anderson LC, Diamond A. Development of cognitive control and executive functions from 4 to 13 years: Evidence from manipulations of memory, inhibition, and task switching. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44(11):2037–78.
22. Faber IR, De Greeff JW, Bostelaar A, Schipper-van Veldhoven N. What moves youth? A survey to explore the motivation and barriers of Dutch young adolescents (12–15 years) to participate in sports. Youth. 2023;3(3):835–46.
23. Ministério da Saúde (BR). Guia alimentar para população brasileira [Internet]. 2ª ed. Brasília (DF): Ministério da Saúde; 2014. 156 p. Available from: <https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/saude-brasil/publicacoes-para-promocao-a-saude/guia_alimentar_populacao_brasileira_2ed.pdf/view> [2024 February]
24. López-Gil JF, García-Hermoso A, Martínez-González MA, Rodríguez-Artalejo F. Mediterranean diet and cardiometabolic biomarkers in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(7):e2421976.
25. Verduci E, Di Profio E, Fiore G, Zuccotti G. Integrated approaches to combatting childhood obesity. Ann Nutr Metab. 2022;78(Suppl 2):8–19.
26. Plavsic L, Knezevic OM, Sovtic A, Minic P, Vukovic R, Mazibrada I, et al. Effects of high-intensity interval training and nutrition advice on cardiometabolic markers and aerobic fitness in adolescent girls with obesity. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(3):294–300.
27. Hanssen H, Moholdt T, Bahls M, Biffi A, Siegrist M, Lewandowski AJ, et al. Lifestyle interventions to change trajectories of obesity-related cardiovascular risk from childhood onset to manifestation in adulthood: a joint scientific statement of the Task Force for Childhood Health of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology and the European Childhood Obesity Group. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023; 30(14):1462–72.
28. Bondyra-Wiśniewska B, Myszkowska-Ryciak J, Harton A. Impact of lifestyle intervention programs for children and adolescents with overweight or obesity on body weight and selected cardiometabolic factors: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4):2061.
29. Jung N, Carpes L, Domingues LB, Abreu R, Ferrari R. Physiological and perceptual demands of singles and doubles beach tennis in women of different competition levels. Front Physiol. 2024;15:1434636.
30. 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee, Dietary Patterns Subcommittee. Dietary patterns and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review [Internet]. Alexandria (VA): USDA Nutrition Evidence Systematic Review; 2020. Available from: <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK578519/> [2024 March].
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dalva Muniz Pereira, Nathalia Nunes Jung, Rodrigo Pedroso, Gabriel Petry Heck, Lorena Isabelle Cerdeira Vieira, Clair Rezende Fontana, Rodrigo Dahmer, Rodrigo Ferrari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
When submitting a manuscript to the Revista Brasileira de Atividade Física & Saúde, the authors retain the copyright to the article and authorize the Revista Brasileira de Atividade Física & Saúde to publish the manuscript under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License and identify it as the original publication source.


