Associations between motivation and different aspects of physical exercise in individuals who maintained weight loss
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12820/rbafs.29e0352Keywords:
Physical activity, Motivation, Weight managementAbstract
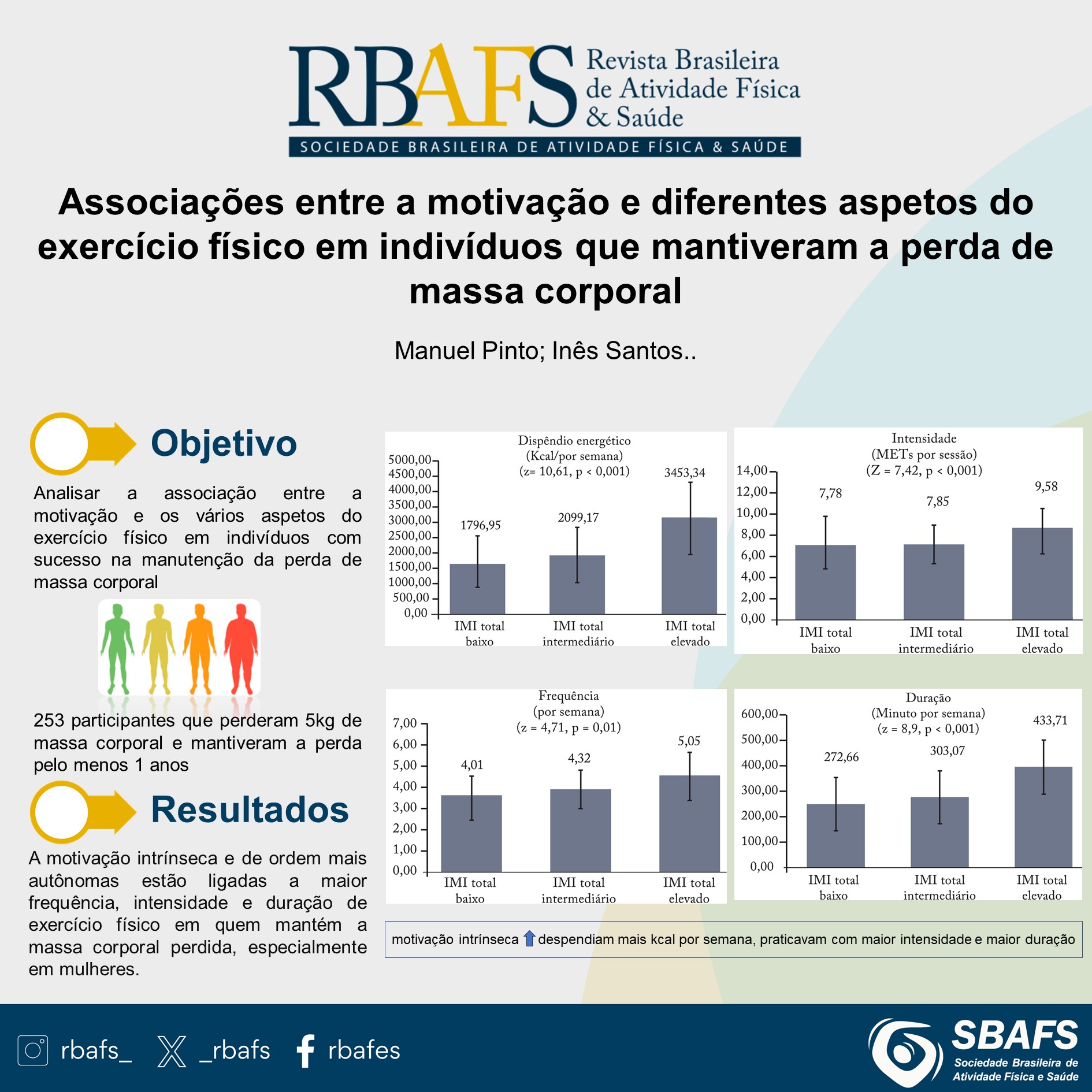
The objective of this study was to analyze the association between motivation and various aspects of physical exercise in individuals who maintained weight loss, and to explore the role of gender. The sample consisted of 253 participants, and their sociodemographic characteristics, body composition, physical exercise, and general and specific motivation for exercise were assessed using validated instruments. The t-test was used to compare various variables between participants. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to analyze the association between motivational variables and different aspects of physical exercise. Motivational variables were divided into tertiles, and the means of various aspects of physical exercise were compared between tertiles using one-way ANOVA. Differences between genders were observed in terms of intensity, duration, energy expenditure, and most motivational variables, favoring males. Positive associations were identified between motivational variables related to exercise, specifically intrinsic motivation and more autonomous regulations, and different aspects of physical exercise in the total sample and among females (p < 0.05). In individuals who successfully maintained weight loss, particularly women, more autonomous motivations for exercise were associated with greater physical exercise. These findings are significant for weight loss and health promotion programs, indicating that autonomous motivation may be a factor in successful weight maintenance.
Downloads
References
Dombrowski SU, Knittle K, Avenell A, Araujo-Soares V, Sniehotta FF. Long term maintenance of weight loss with non-surgical interventions in obese adults: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2014;348:g2646. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g2646. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g2646
Franz MJ, VanWormer JJ, Crain AL, Boucher JL, Histon T, Caplan W, et al. Weight-loss outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of weight-loss clinical trials with a minimum 1-year follow-up. J Am Diet Assoc. 2007;107(10):1755-67. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2007.07.017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2007.07.017
Spreckley M, Seidell J, Halberstadt J. Perspectives into the experience of successful, substantial long-term weight-loss maintenance: a systematic review. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2021;16(1):1862481. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/17482631.2020.1862481. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17482631.2020.1862481
MacLean PS, Bergouignan A, Cornier MA, Jackman MR. Biology’s response to dieting: the impetus for weight regain. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;301(3):R581-600. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00755.2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00755.2010
Teixeira PJ, Marques M, Carraça EV, Rutter H, Oppert JM, De Bourdeaudhuij I, et al. A systematic review of self-regulation mediators of success in obesity interventions: the SPOTLIGHT project. The European Health Psychologist. 2015;17(S):440.
Fogelholm M, Kukkonen-Harjula K. Does physical activity prevent weight gain--a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2000;1(2):95-111. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1467-789x.2000.00016.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1467-789x.2000.00016.x
Paixão C, Dias CM, Jorge R, Carraça EV, Yannakoulia M, de Zwaan M, et al. Successful weight loss maintenance: A systematic review of weight control registries. Obes Rev. 2020;21(5):e13003. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13003. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13003
Santos I, Vieira PN, Silva MN, Sardinha LB, Teixeira PJ. Weight control behaviors of highly successful weight loss maintainers: the Portuguese Weight Control Registry. J Behav Med. 2017;40(2):366-71. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-016-9786-y.
Elfhag K, Rössner S. Who succeeds in maintaining weight loss? A conceptual review of factors associated with weight loss maintenance and weight regain. Obes Rev. 2005;6(1):67-85. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2005.00170.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2005.00170.x
Ryan RM, Deci EL. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am Psychol. 2000;55(1):68-78. doi: https://doi.org/10.1037//0003-066x.55.1.68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037//0003-066X.55.1.68
Ryan RM, Williams GC, Patrick H, Deci EL. Self-determination theory and physical activity: The dynamics of motivation in development and wellness. Hellenic Journal of Psychology. 2009;6:107-24.
Santos I, Silva MN, Teixeira PJ. A self-determination theory perspective on weight loss maintenance. The European Health Psychologist. 2016;18(5):194-99.
Duncan LR, Hall CR, Wilson PM, Jenny O. Exercise motivation: a cross-sectional analysis examining its relationships with frequency, intensity, and duration of exercise. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2010;7:7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-7-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-7-7
Santos I, Vieira PN, Silva MN, Sardinha LB, Teixeira PJ. Weight control behaviors of highly successful weight loss maintainers: the Portuguese Weight Control Registry. J Behav Med. 2017;40(2):366-71. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-016-9786-y. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-016-9786-y
Blair SN, Haskell WL, Ho P, Paffenbarger RS, Vranizan KM, Farquhar JW, Wood PD. Assessment of habitual physical activity by a seven-day recall in a community survey and controlled experiments. Am J Epidemiol. 1985;122(5):794-804. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114163. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114163
Gross LD, Sallis JF, Buono MJ, Roby JJ, Nelson JA. Reliability and validity of self-reported physical activity with accelerometer validation in adolescents. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1990;61(1):47-53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/02701367.1990.10607494
Sheldon KM, Deci EL. The Self-Determination Scale. In: Manual: A new measure of motivation and satisfaction. Rochester, NY: University of Rochester; 1996.
Deci EL, Ryan RM. The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychol Inq. 2000;11(4):227-68. doi: https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01
Markland D, Tobin VJ. A modification to the Behavioural Regulation in Exercise Questionnaire to include an assessment of amotivation. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2004;26(2):191-96. doi: https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.26.2.191. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.26.2.191
McAuley E, Duncan T, Tammen VV. Psychometric properties of the Intrinsic Motivation Inventory in a competitive sport setting: A confirmatory factor analysis. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1989;60(1):48-58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/02701367.1989.10607413. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/02701367.1989.10607413
Ryan RM. Control and information in the intrapersonal sphere: An extension of cognitive evaluation theory. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1982;43(3):450-61. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.43.3.450
Lumley T, Diehr P, Emerson S, Chen L. The importance of the normality assumption in large public health data sets. Annu Rev Public Health. 2002;23:151-69. doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.23.100901.140546. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.23.100901.140546
Ryan RM, Deci EL. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: Classic definitions and new directions. Contemp Educ Psychol. 2000;25(1):54-67. doi: https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1999.1020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1999.1020
Deci EL, Ryan RM. Self-determination theory: A macrotheory of human motivation, development, and health. Can Psychol. 2008;49(3):182-85. doi: https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012801 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012801
Edmunds J, Ntoumanis N, Duda JL. A test of self-determination theory in the exercise domain. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2006;18(5):495-505. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0021-9029.2006.00102.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0021-9029.2006.00102.x
Teixeira PJ, Carraça EV, Markland D, Silva MN, Ryan RM. Exercise, physical activity, and self-determination theory: A systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2012;9(1):78. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-9-78. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-9-78
Wilson PM, Rodgers WM, Blanchard CM, Gessell J. The relationship between psychological needs, self-determined motivation, exercise attitudes, and physical fitness. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2003;33(11):2373-92. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2003.tb01890.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2003.tb01890.x
Kowal J, Fortier MS. Motivational determinants of flow: Contributions from self-determination theory. J Soc Psychol. 1999;139(3):355-68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00224549909598391
Ingledew DK, Brunning S. Personality, preventive health behaviour and comparative optimism about health problems. J Health Psychol. 1999;4(2):193-208. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/135910539900400213. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/135910539900400213
Brick N, MacIntyre TE. Associations between psychological factors and performance during a cross-country mountain running race in elite athletes. J Sports Sci. 2012;30(9):931-37.
Sebire SJ, Standage M, Vansteenkiste M. Examining intrinsic versus extrinsic exercise goals: Cognitive, affective, and behavioral outcomes. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2009;31(2):189-210. doi: https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.31.2.189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.31.2.189
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Manuel Pinto, Inês Santos

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
When submitting a manuscript to the Revista Brasileira de Atividade Física & Saúde, the authors retain the copyright to the article and authorize the Revista Brasileira de Atividade Física & Saúde to publish the manuscript under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License and identify it as the original publication source.


